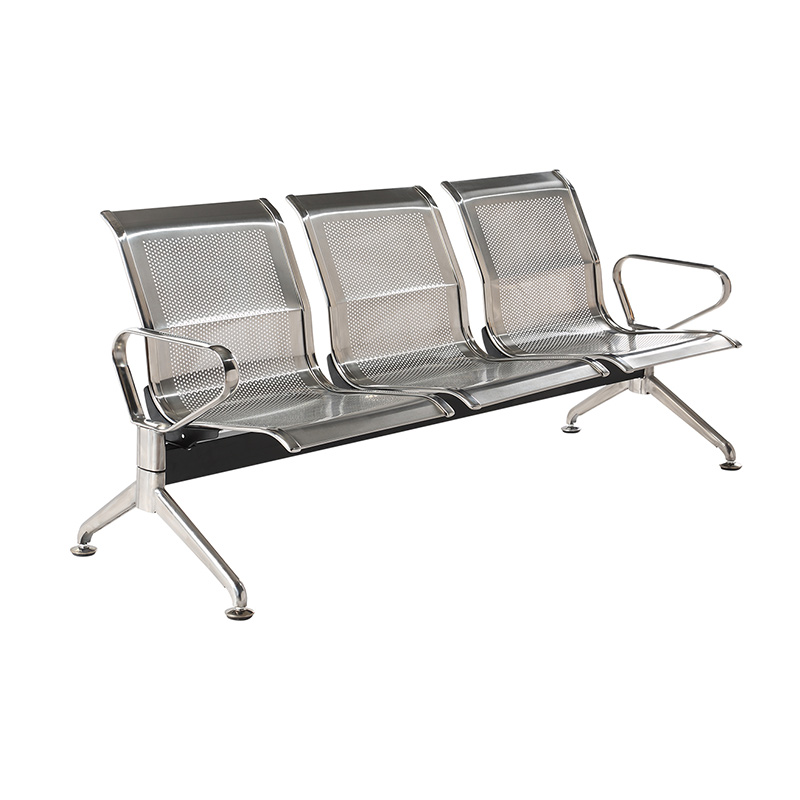
What Material Are Hospital Chairs Made Of?
Hospital chairs are a quiet yet essential part of healthcare design. They carry more than just people—they carry trust, comfort, and hygiene. Every surface, joint, and material choice is deliberate, balancing durability, safety, and sanitation. Unlike ordinary furniture, hospital chairs face constant use, frequent cleaning, and strict health standards. The materials chosen must withstand these challenges while supporting patients, visitors, and medical staff with reliability and ease.
This article explores the main materials used in hospital chair manufacturing, examining their properties, applications, and the reasons behind each choice.
1. Stainless Steel — The Backbone of Hygiene and Strength
Among all materials, stainless steel remains the foundation of hospital chair design. Known for its durability, non-corrosive nature, and sleek appearance, stainless steel meets the strict hygiene and maintenance standards demanded by healthcare environments.
The most common grade used is SUS304, which provides a high level of corrosion resistance due to its chromium and nickel composition. It resists oxidation even after years of exposure to disinfectants and moisture. For intensive-use areas, SUS316 may be chosen for its superior resistance to chemicals and salt environments, often seen in coastal hospitals.
Advantages:
Anti-bacterial and non-porous surface: Prevents microorganisms from breeding, even in humid conditions.
Easy to clean: Can be wiped with alcohol or chlorine-based cleaners without damage.
High mechanical strength: Suitable for heavy-duty seating like Waiting Chairs and stretchers.
Fire-resistant: Maintains integrity under high temperature and sterilization conditions.
Designers often prefer brushed or matte finishes to minimize glare from medical lighting. The material’s ability to combine functionality with modern aesthetics makes it a staple for frames, legs, and armrests in hospital seating systems.
2. Aluminum Alloy — Lightweight Efficiency for Modern Healthcare
As hospitals expand and redesign for mobility and modularity, aluminum alloy has become a preferred alternative to heavier metals. Aluminum’s greatest strength lies in its light weight and adaptability. It is strong enough to support daily use yet easy to transport and reconfigure across departments.
Key Characteristics:
Lightweight yet durable: Reduces strain during transport and relocation.
Corrosion-resistant: Naturally forms a protective oxide layer.
Excellent recyclability: Aligns with the growing push toward sustainable healthcare facilities.
In hospital waiting areas, aluminum frames support linked seats or modular units. Its smooth surface accepts powder coating, which not only enhances color options but also adds a protective barrier against cleaning agents and scratching.
Moreover, aluminum’s thermal conductivity helps it adjust quickly to room temperature, making it more comfortable for patients to touch in varying climates. The combination of strength, appearance, and practicality ensures aluminum continues to play a growing role in hospital chair design, especially in modern architectural environments that value sleek, minimalist finishes.
3. High-Density Polypropylene (PP) — The King of Cleanability
Another dominant material in healthcare seating is high-density polypropylene (PP), a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness and chemical resistance. It is widely used in the seat shells, backrests, and arm components of Hospital Waiting Chairs, wheelchairs, and visitor seating.
Polypropylene’s popularity stems from its balance between affordability and hygiene. It is inherently non-porous, resists staining, and can endure daily cleaning with disinfectants such as bleach or alcohol without fading or cracking.
Performance Highlights:
Chemical-resistant: Withstands continuous exposure to disinfectants.
Molded design flexibility: Enables ergonomic shapes that enhance comfort and posture support.
Impact-resistant: Prevents cracks even under heavy use in crowded waiting areas.
Color-integrated surfaces: Pigment is embedded during molding, reducing the need for painting and preventing surface peeling.
Hospitals value polypropylene for its cost-efficiency and ease of mass production. The material is often paired with metal frames for added stability, creating chairs that are both durable and visually cohesive. In pediatric or outpatient zones, colorful PP seating also helps reduce the sterile appearance of medical environments and creates a friendlier, more human atmosphere.
4. Upholstered Fabric and Synthetic Leather — Balancing Comfort and Hygiene
Not all hospital chairs are purely metallic or plastic. In areas such as patient rooms, lounges, and consultation zones, upholstered materials are used to enhance comfort while maintaining hygiene standards. These materials include medical-grade synthetic leather (PVC or PU) and specialized woven fabrics treated for antimicrobial protection.
Synthetic Leather (PU/PVC)
PU (polyurethane) and PVC (polyvinyl chloride) upholstery combine softness with practicality. Both are waterproof, flame-retardant, and resistant to alcohol-based cleaning solutions. PU offers a softer, more leather-like feel, while PVC provides superior resistance to moisture and discoloration.
Their sealed surfaces prevent liquid absorption, an essential feature in hospitals where sanitation and quick cleanup are critical. This makes synthetic leather ideal for infusion chairs, dialysis seating, and visitor Sofas.
Woven Fabrics
High-performance woven fabrics coated with anti-microbial or anti-fungal finishes are gaining traction in waiting lounges and rehabilitation zones. They allow better breathability than synthetic leather and can now match medical-grade hygiene standards through advanced coatings.
| Upholstery Type | Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PU (Polyurethane) | Soft, breathable, eco-friendly | Outpatient waiting areas, infusion chairs |
| PVC (Vinyl) | Highly waterproof, chemical-resistant | Emergency departments, patient lounges |
| Antimicrobial Fabric | Comfortable, breathable, resistant to bacteria | VIP wards, rehab centers |
These materials combine the comfort of hospitality furniture with the durability and sanitation required in healthcare.
5. Foam and Cushioning — The Science of Support
Underneath every comfortable hospital chair lies a layer of engineered foam. The choice of foam density and composition determines long-term comfort, pressure relief, and durability. Hospitals increasingly adopt medical-grade polyurethane foam and memory foam for patient and waiting area seating.
Key Features:
Density control: Foam density between 35–50 kg/m³ ensures both resilience and support.
Flame retardancy: Certified foams meet international standards such as CAL TB117 or EN1021 for fire safety.
Moisture barrier films: Prevent absorption of fluids and enhance hygiene.
In patient and dialysis chairs, multi-layer foams combine soft upper layers for comfort with firm lower layers for stability. Some designs also include gel-infused cushions to prevent heat buildup and improve pressure distribution for long-term sitting.
To further ensure cleanliness, the foam is sealed within a waterproof liner before upholstery application. This design minimizes bacterial growth and extends the product’s usable life. The innovation in cushioning materials shows how hospitals now value patient experience as much as medical efficiency.
Conclusion
Hospital chairs are crafted not just from metal and plastic, but from a deep understanding of function, hygiene, and human comfort. From the enduring strength of stainless steel to the lightness of aluminum, from the easy maintenance of polypropylene to the softness of synthetic leather, each material plays a unique role in creating a safe and welcoming healthcare environment.
Modern trends emphasize sustainability, modularity, and patient well-being. Materials are now chosen not only for endurance but also for their ability to support healing and calmness. As technology advances, the hospital chair evolves into something more than a place to sit—it becomes part of the care experience itself.
The next generation of hospital chairs will continue to reflect this balance between science, comfort, and design, shaping spaces where patients and visitors feel truly supported—physically and emotionally.
Previous: Airport Chairs Design Trends